Obstructive sleep apnea
Sleep disordersSleep apnea
What is it ?
Sleep apnea causes breathing to repeatedly stop for longer than 10 seconds during sleep. In rare cases, these pauses can even exceed one minute. Sleep apnoea syndrome is diagnosed when a patient experiences at least 5 apnoea events per hour of sleep.
According to the HypnoLaus study (mettre un lien) carried out in Switzerland, this widespread pathology affects 49% of men and 23% of women over the age of 40. However, due to a lack of awareness about its symptoms, many people remain undiagnosed and untreated.
The different types of sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSA)
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSA) is a breathing disorder characterised by partial (hypopnea) or complete (apnea) obstruction of the upper airways for at least 10 seconds resulting in repeated drops in oxygen levels. Despite this obstruction, the lungs’ respiratory effort is maintained.
Central sleep apnea syndrome (CSA)
Central sleep apnea syndrome (CSA) is a breathing disorder characterised by a dysfunctional nerve command that no longer prompts inspiratory muscles. This disorder induces episodes of central sleep apnea and/or hypopnea. Patients with central sleep apnea often also have obstructive sleep apnea.
The consequences of sleep apnea
In addition to fatigue, daytime sleepiness and memory problems caused by sleep apnea, the consequences in terms of health and quality of life should not be underestimated.
People with sleep apnea syndrome often experience excessive daytime sleepiness and an increased risk of accidents. Their quality of life may also be affected: poor performance at work, irritability, deterioration of social relationships, sexual dysfunction, etc.
Moreover, it has been demonstrated that sleep apnea is a risk factor for developing cardiovascular pathologies such as high blood pressure, strokes or cardiac rhythm disorders.
Sleep apnea can also lead to pain, depression and inflammatory diseases, contribute to weight gain (lien page nutrition et sommeil) and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Warning signs and symptoms
- Sensation of non-restorative sleep
- Fatigue
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
And also...
These symptoms should always be considered as signs of a potential sleep disorder. And sleep apnoea is no exception to the rule.
Furthermore, the other signs to look for are frequent snoring, breathing pauses during sleep (often perceived by the subject’s spouse), excessive night-time sweating, dry mouth and thirst, morning headaches, need to urinate several times during the night as well as reduced sex drive.
Download the brochure
Learn more
Polysomnography
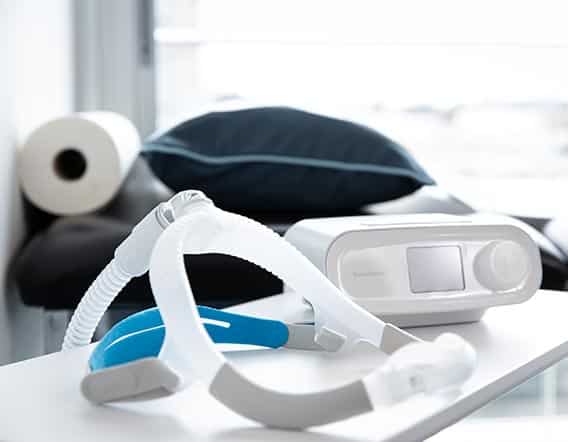
Treatment of sleep apnea

 Share on facebook
Share on facebook
 Share on twitter
Share on twitter
 Share on linkedin
Share on linkedin
 Share by email
Share by email